How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to stunning aerial photography, innovative surveying, and exciting recreational pursuits. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone piloting, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety regulations to advanced flight techniques and post-flight procedures. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, camera operation, and flight planning, ensuring you gain a comprehensive understanding of responsible drone operation.
From understanding basic maneuvers to mastering advanced flight modes and camera settings, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies responsibly. We’ll also delve into the legal and ethical considerations surrounding drone use, emphasizing the importance of safe and respectful flight practices.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight check and adherence to safety regulations are paramount. This ensures both the safety of the drone and those in its vicinity. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and legal repercussions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves a systematic check of all critical drone components. This minimizes the risk of malfunctions during flight. The following table Artikels key components and their respective checkpoints:
| Component | Check | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or loose attachments. | Replace damaged propellers immediately. | |
| Battery | Check battery level and ensure proper connection. | Use a fully charged battery for optimal flight time. | |
| Motors | Visually inspect for any damage or debris. | Listen for unusual noises during motor spin-up. | |
| GPS System | Ensure GPS signal is strong and stable. | Sufficient satellites are required for accurate positioning. | |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Clean the lens if necessary. | |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check for smooth movement and proper functionality. | Ensure gimbal is securely mounted. | |
| Radio Control System | Test the responsiveness of all controls. | Check for signal interference. | |
| Airframe | Inspect for any damage or loose parts. | Pay close attention to structural integrity. |
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and best practices. These regulations often vary by location, so it is crucial to research the specific rules in your area before flying.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Avoid flying near airports, heliports, or other restricted airspace.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Never fly your drone under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
- Keep your drone’s firmware updated for optimal performance and safety.
Calculating Safe Flight Distances, How to operate a drone
Maintaining safe distances from obstacles and people is critical. A simple method involves considering the drone’s maximum range and the potential for loss of control. Always add a significant safety margin.
- Determine your drone’s maximum range.
- Identify all potential obstacles within the flight area.
- Calculate the minimum safe distance based on the drone’s size and speed.
- Add a safety buffer of at least 50% to this distance.
- Maintain this distance throughout the flight.
Flight Delay or Cancellation Decision-Making
Weather conditions and other factors can significantly impact flight safety. A decision-making flowchart helps determine whether to delay or cancel a flight.
[A flowchart would be inserted here visually depicting the decision-making process based on wind speed, precipitation, visibility, and other relevant factors, leading to either “Proceed with Flight” or “Delay/Cancel Flight” as the final decision points.]
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation

Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different drones may have slightly varying controls, but the basic principles remain consistent.
Drone Controller Functions
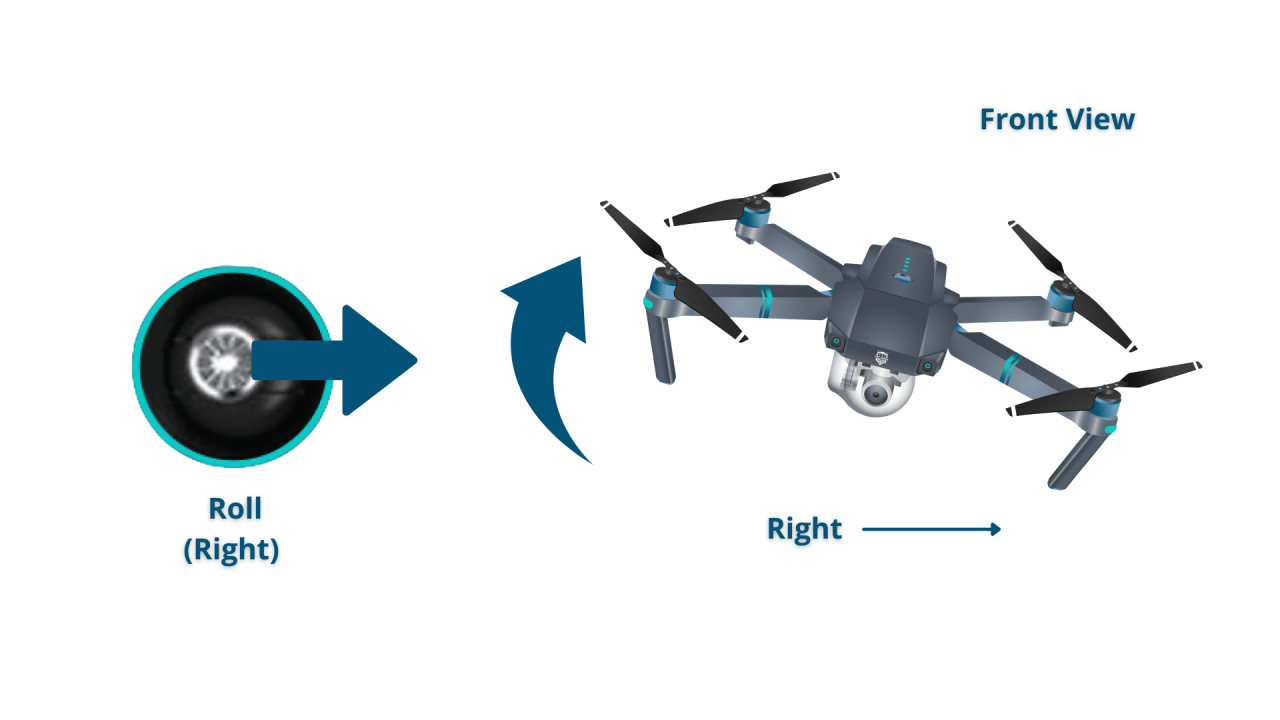
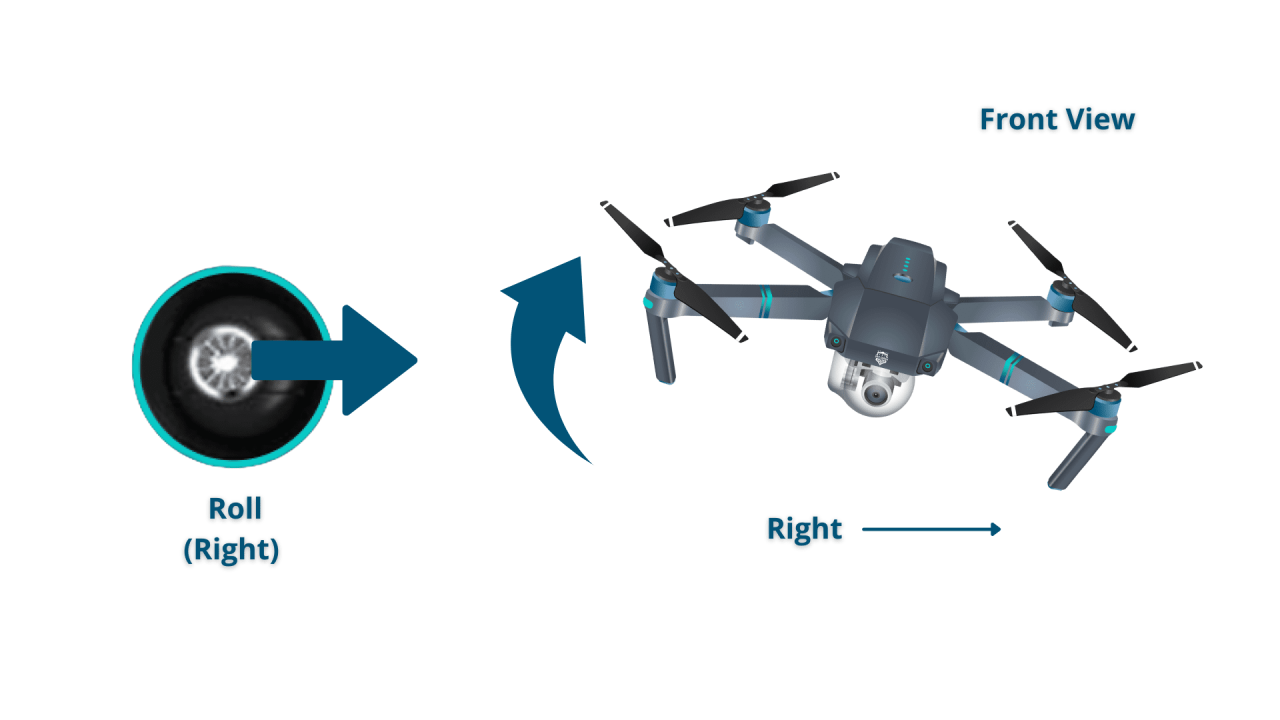
A typical drone controller features two joysticks and several buttons. The left joystick generally controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick controls roll (tilting) and pitch (forward/backward movement). Buttons typically control functions like taking off, landing, returning to home, and switching flight modes.
Flight Modes
Drones offer various flight modes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these modes is crucial for adapting to different flying conditions.
- GPS Mode: Relies on GPS signals for position and stability, offering smoother and more predictable flight. Suitable for long-range flights and precise maneuvers.
- Attitude Mode (Atti Mode): Relies on the drone’s internal sensors for orientation and stability. Useful in GPS-denied environments or for quick, agile maneuvers, but requires more pilot skill.
- Sport Mode (if applicable): Generally increases responsiveness and speed, ideal for dynamic aerial shots but requires advanced piloting skills.
GPS vs. Non-GPS Flight
GPS-enabled drones offer greater stability and precision, particularly during longer flights. However, they rely on a clear GPS signal, which can be affected by weather or obstacles. Non-GPS drones offer greater agility but require more skill to control, especially in windy conditions.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is essential before attempting more complex flights. These maneuvers form the foundation of proficient drone piloting.
- Taking Off: Initiate takeoff sequence using the controller’s designated button or stick combination.
- Landing: Initiate landing sequence using the controller’s designated button or stick combination.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air by carefully adjusting the controls.
- Moving in Different Directions: Use the joysticks to control the drone’s movement forward, backward, left, right, up, and down.
Flight Planning and Mission Execution
Effective flight planning is crucial for successful aerial photography or videography missions. A well-defined plan ensures efficient use of battery power and minimizes the risk of accidents.
Sample Flight Plan for Aerial Photography
This example demonstrates a basic flight plan for capturing aerial photos of a park.
- Waypoint 1: Takeoff point (10 meters altitude).
- Waypoint 2: Fly to the center of the park (20 meters altitude), capturing photos.
- Waypoint 3: Fly along the park’s perimeter (20 meters altitude), capturing photos.
- Waypoint 4: Return to the takeoff point (10 meters altitude).
- Waypoint 5: Land.
Setting Up and Executing a Pre-Programmed Flight Path
Many drone apps allow for pre-programming flight paths using waypoints and altitude settings. This ensures consistent and repeatable flights.
- Plan your flight path using the drone’s app.
- Set waypoints and altitudes.
- Review the flight plan to ensure accuracy.
- Upload the flight plan to the drone.
- Initiate the automated flight.
- Monitor the flight and intervene if necessary.
Managing Battery Life
Efficient battery management is crucial for extended flights. Factors such as wind speed, altitude, and payload significantly impact battery consumption.
- Use a fully charged battery.
- Avoid aggressive maneuvers that consume more power.
- Plan for sufficient flight time, considering the battery’s capacity.
- Bring extra batteries for longer flights.
Challenges in Flight Planning and Solutions
Flight planning may encounter various challenges, including unexpected weather changes or GPS signal loss. Preparation and contingency planning are essential.
- Challenge: Unexpected wind gusts. Solution: Delay or cancel the flight; adjust flight parameters to compensate.
- Challenge: GPS signal loss. Solution: Switch to a suitable alternative flight mode, or land immediately.
- Challenge: Low battery warning. Solution: Initiate a return-to-home sequence; land immediately.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture

Understanding camera settings and techniques is vital for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. Proper settings can significantly enhance image quality and aesthetic appeal.
Camera Settings and Their Impact
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture influence image brightness, sharpness, and depth of field. Understanding their interplay is key to capturing desired results.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Learning how to navigate effectively is key, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable flying experience.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values are ideal for bright conditions, while higher values are suitable for low-light situations, but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, while a narrower aperture (larger f-number) creates a deeper depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Achieving high-quality aerial imagery requires careful consideration of various factors, including lighting, composition, and camera settings.
- Shoot during the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Use a tripod or gimbal for stabilization.
- Experiment with different camera settings to find what works best for your specific conditions.
- Keep the drone stable to minimize camera shake.
Image Stabilization and Minimizing Camera Shake
Image stabilization is critical for sharp, clear images and videos. Several techniques can help minimize camera shake.
- Use a gimbal for smooth footage.
- Fly smoothly and avoid jerky movements.
- Adjust camera settings to compensate for wind or other disturbances.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Creative composition is essential for impactful aerial imagery. Framing and perspective play key roles in creating visually engaging shots.
- Use leading lines to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Pay attention to the rule of thirds for balanced compositions.
Post-Flight Procedures and Data Management: How To Operate A Drone
Proper post-flight procedures and data management are crucial for maintaining your drone and preserving valuable footage. These steps ensure the longevity of your equipment and the safety of your data.
Landing and Securing the Drone
Safe and controlled landing is paramount. Always choose a suitable landing area, free from obstacles and hazards.
- Select a level and clear landing area.
- Initiate the landing sequence using the controller.
- Once landed, power off the drone and remove the battery.
- Inspect the drone for any damage.
- Store the drone in a safe and protective case.
Downloading and Organizing Drone Footage and Photos
Efficiently downloading and organizing your drone data ensures easy access and prevents loss of valuable content.
- Connect the drone to your computer or mobile device.
- Download all footage and photos.
- Create a well-organized folder structure for storing your media.
- Rename files with descriptive names and dates.
Storing and Backing Up Drone Data
Data loss can be devastating. Implementing a robust backup strategy is crucial.
- Store your data on multiple hard drives or cloud storage.
- Regularly back up your data to prevent loss.
- Consider using RAID systems for enhanced data redundancy.
Post-Flight Maintenance and Inspection Checklist
Regular post-flight maintenance is essential for the longevity and reliability of your drone. This checklist helps ensure a thorough inspection.
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Check motor mounts for tightness.
- Inspect the airframe for cracks or damage.
- Clean the drone body and camera lens.
- Store the drone in a safe and dry place.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Despite careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. Understanding common issues and their solutions can minimize downtime and frustration.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
This section provides solutions for resolving frequently encountered drone problems.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully. Use a fully charged battery for your next flight.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure clear skies and a strong GPS signal. Relocate to an area with better reception. Consider using an alternative flight mode if available.
- Motor Failure: Inspect motors for damage or debris. Replace faulty motors.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Check gimbal for proper mounting and functionality. Recalibrate the gimbal if necessary. Contact support for assistance if needed.
- Controller Connectivity Issues: Check battery levels on both drone and controller. Ensure there is no signal interference. Try re-pairing the drone and controller.
Handling Emergency Situations
Unexpected events can occur. Knowing how to respond to emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation.
- Unexpected Power Loss: Initiate return-to-home sequence (if available). Attempt to land the drone safely in a clear area.
- Loss of Control: Attempt to regain control by adjusting the controls smoothly. If unsuccessful, initiate a return-to-home sequence or attempt an emergency landing.
[A troubleshooting flowchart would be inserted here, guiding users through a systematic process of diagnosing and resolving drone problems based on observed symptoms and error messages.]
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Drone operation involves legal and ethical responsibilities. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines ensures responsible and safe drone use.
Airspace Regulations and Restrictions
Airspace regulations vary widely depending on location and specific circumstances. Familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations before operating a drone.
- Register your drone with the appropriate authorities (where required).
- Obtain necessary permits for commercial drone operations.
- Avoid flying near airports, heliports, or other restricted airspace.
- Maintain a safe distance from people and property.
Ethical Implications of Drone Usage
Responsible drone operation involves respecting the privacy of others and being mindful of potential societal impacts.
- Avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Respect individuals’ privacy and avoid recording people without their consent.
- Be aware of the potential for misuse and act responsibly.
Scenarios Where Drone Use Might Be Problematic
Certain scenarios present legal or ethical challenges. Careful consideration is required before operating a drone in these situations.
- Flying near emergency response sites.
- Recording individuals without their consent.
- Flying in areas with restricted airspace.
Resources for Local Drone Regulations
Several resources provide information on local drone regulations. Consulting these resources ensures compliance with the law.
- Your country’s aviation authority website.
- Local government websites.
- Drone pilot associations and communities.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical skill, responsible decision-making, and a deep understanding of safety protocols. By diligently following the pre-flight checks, understanding your drone’s capabilities, and adhering to all regulations, you can unlock the potential of aerial technology while minimizing risks. Remember, consistent practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Enjoy the skies!
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires practice and a solid understanding of safety regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, responsible and skillful drone operation ensures safe and effective flights.
FAQ
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automatic flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functionality.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced interference.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during a flight?
If GPS is lost, immediately switch to Atti mode (attitude mode), carefully maneuver the drone back to a safe landing area, and land it smoothly.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
Can I fly my drone in rain or strong winds?
No, never fly your drone in inclement weather. Rain and strong winds can damage the drone and create unsafe flying conditions.